What Is Data Scraping: Uses & Examples
The extraction of data from various online sources has become a crucial practice for businesses, researchers, and individuals alike. This process, known as data scraping, involves retrieving information from websites and other digital platforms. It serves as a fundamental method for accessing valuable insights, driving decision-making, and fostering innovation.
In this article, we explore what is data scraping, its practical applications, its process, as well as its legal considerations.
What is Data Scraping?
Data scraping, also known as web scraping or data extraction, is the automated process of gathering information from websites and other online sources. It involves retrieving specific data elements, such as text, images, or files, from web pages and structuring them into a usable format for analysis or storage.
Unlike manual data collection methods, which can be time-consuming and error-prone, data scraping utilizes software tools and algorithms to automate retrieval. These tools access web pages, extract the desired data, and organize it according to predefined criteria, streamlining the data acquisition process and enabling rapid information retrieval at scale.
How is Data Scraping done?
Various techniques are commonly employed to scrape data from websites. Generally, these techniques involve retrieving content from websites, processing it using a scraping engine, and generating one or more data files with the extracted content.
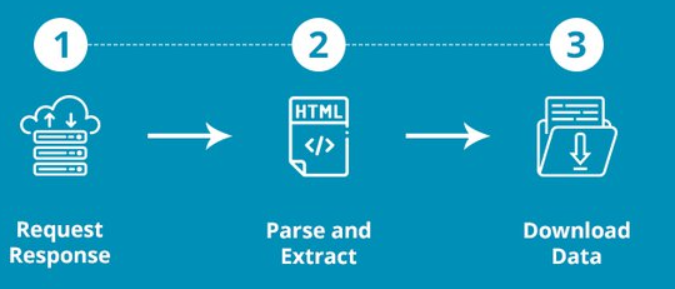
Some techniques include:
What is Data Scraping used for?
Data scraping can be used for a wide range of purposes, depending on how you process and analyze it. Here are some of the most common business use cases for data scraping.
Consumer Sentiment Analysis
The success of any product or service relies heavily on how customers perceive it. You can gain valuable insights into how customers see your offerings by strategically gathering reviews, comments, and discussions from online platforms. Combining this data gives you a clear picture of the overall positive, neutral, or negative sentiments, allowing you to refine your products or services, address customer concerns directly, and capitalize on your strengths. This essentially creates a feedback loop, enabling brands to maintain a strong reputation and better serve their customer base.
Brand, Product, And Price Monitoring
This is for businesses wanting to track their brands and competitors' online presence. Data scraping offers a high-volume solution for monitoring everything from social media mentions to ongoing promotions and pricing strategies. By leveraging data scraping to gather real-time information, businesses can make strategic adjustments and adapt their approach as needed.
Market Research
Data scraping allows you to collect a vast amount of data on your competitors, current market trends, and evolving consumer preferences. Once this data is cleaned, processed, and analyzed, it can provide valuable insights. These insights can guide your marketing campaigns and strategies. It can also unveil gaps in the market and predict upcoming trends, ultimately propelling your efforts forward.
Lead Generation
You can discover potential high-value clients by automating the process of extracting valuable information from professional networks, online directories, and industry-specific websites. This proactive approach gives sales and marketing teams a head start by identifying promising leads beforehand. Utilizing data scraping techniques and applying analytical models helps you connect with the most relevant prospects efficiently, saving valuable time compared to manual searching.
What is the Difference between Data Scraping and Mining?
Before diving into data scraping and mining, let's understand how they differ and work together. Data scraping is like collecting data from the Internet, while data mining is about finding useful information from that data. To make it clearer, let's compare them in the table below.
Data Scraping Examples
Data scraping has a variety of applications across different industries. Here are some examples:
Real Estate Data Analysis
If you're in the real estate industry, web scraping can be a valuable tool for analyzing property listings and prices. By extracting and analyzing data from real estate websites, you can gain insights into properties that help you make better decisions. Companies like OpenDoor use web scraping to provide homeowners with property sale quotes, making the process more efficient and transparent.
Travel Industry Data Aggregation
In the competitive travel sector, using web scraping facilitates aggregating data from various travel websites to offer comprehensive comparisons. Kayak, for example, extracts pricing and availability data to assist tourists in finding the best deals.
Logistics and Product Delivery Optimization
For supply chain optimization, logistics companies use web scraping to gather shipping rates, delivery times, and customer reviews. FedEx utilizes scraped data to provide real-time package tracking information, improving transparency and customer satisfaction.
Is Data Scraping Legal?
The legality of data scraping depends on various factors, including the method used, the source of the data, and the purpose of scraping. In many cases, scraping public data from websites where there are no explicit terms of service prohibiting it is considered legal. However, scraping data from websites that have implemented measures to prevent scraping or have terms of service explicitly prohibiting it may be illegal and could result in legal action.
Additionally, scraping data that is protected by copyright or contains personal or sensitive information may also be illegal. It's important to confirm compliance with relevant laws and regulations, such as copyright law, data protection laws (e.g., GDPR), and the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the United States.
It's recommended that you review the terms of service of websites from which you intend to scrape data and obtain permission if necessary. Employing ethical scraping practices, respecting website policies, and avoiding excessive or disruptive scraping behavior can help mitigate legal risks associated with data scraping. Consulting with legal experts familiar with data scraping laws and regulations in your jurisdiction may provide further guidance on ensuring compliance.
Conclusion
We have learned what is data scraping and how it enables businesses, researchers, and individuals to make informed decisions and drive innovation. By automating the process of gathering and structuring data from websites, data scraping streamlines information retrieval and facilitates analysis at scale.
From lead generation to brand monitoring or sentiment analysis, data scraping finds applications across various industries, helping to stay competitive and responsive to trends. However, it's essential to approach data scraping ethically and legally, respecting the rights and policies of data sources and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
Comments
Post a Comment